- For the growth of the foetus and the placenta.
- To add to your fat reserves.
- To balance the energy used by a higher basal metabolic rate and the work you do carrying the baby.
You should increase your daily food intake by an additional 1 200 kilojoules.
Too little weight gain
Too little weight gain can lead to, or be the result of, complications. It may be associated with an increased risk of developing pregnancy hypertension or pre-eclampsia, and delivering a low birth weight baby. Pregnancy is not a time for starting a weight-loss diet, as it may lead to ketosis (burning of body fat). The by- product of ketosis can damage the foetus.
Too much weight gain
Too much weight gain increases the risk of complications during delivery. The overweight baby has a higher rate of complications soon after birth.
Increased weight distribution
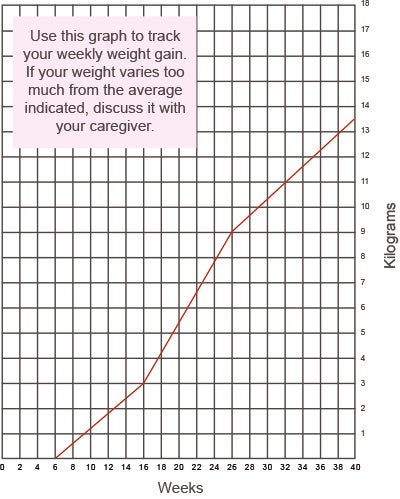
Weight gain over trimesters
Typically a mother gains 1- 2kg by the end of the first trimester, and thereafter about 0,5 kg each week. The recommended weight gain for a healthy woman during the 40 weeks of her pregnancy is approximately 12–14 kg.
General guidelines
- Foods should be carefully cooked. Grilling, steaming and stir-frying are preferable to roasting, frying and boiling. Try to cook lightly to preserve nutrient value.
- Frequent small meals are better than large meals. They are easier to digest and you will feel less uncomfortable.
- Eat a wide variety of foods.
- Use normal amounts of iodised salt.
- Drink at least eight glasses of water per day.
- Take foods containing iron with foods containing vitamin C, as vitamin C helps absorb iron. Ideally, build up your iron supply before pregnancy.
- It is useful to keep a record of what you eat over a 24–48 hour period.
- If you are worried about your diet, consult your caregiver.

| Fats, oils, sugars | sparingly |
| Meat, poultry, fish, legumes | 2-3 servings |
| Milk, yoghurt, cheese | 2-3 servings |
| Vegetables Fruit | 3-5 servings 2-4 servings |
| Bread, cereal, rice, pasta | 4 or more servings |
| HEALTH DIET PYRAMID | |
Nutrients you need
| Food groups | Main nutrients | Amount per serving |
Servings per day while pregnant |
Servings per day while breastfeeding |
| Cereals, grains | 4 or more | 4 or more | ||
| Bread, whole grain or enriched |
Carbohydrate | 1 slice | ||
| Cooked cereal | Thiamin | 1/2 – 3/4 cup | ||
| Pasta | Iron | 1/2 – 3/4 cup | ||
| Rice | Niacin | 1/2 – 3/4 cup | ||
| Dry cereal | 30 g | |||
| Vegetables fruit |
4 or more | 4 or more | ||
| Vegetables, cooked or raw |
Vitamin A | 1/2 cup | ||
| Fruits, fresh | Vitamin C | 1 med, 1/2 large |
1 vitamin C – citrus juice |
1 vitamin C – citrus juice |
| Juices, fresh or canned |
1/2 cup | |||
| Potato | Carbohydrate | 1 | ||
| Salad, green | bowl | 1 deep-yellow/ dark green vegetable |
1 deep-yellow/ dark green vegetable |
|
| Dairy group | 2–3 | 3-4 | ||
| Milk, low-fat | Vitamin D | 225 g (1 cup) | ||
| Yoghurt, plain | Calcium | 1 cup | ||
| Hard cheese | Riboflavin | 37 g | ||
| Cottage cheese |
Protein | 2 cups | ||
| Meat, other proteins |
2 | 3 | ||
| Meat, lean | Protein | 60–90 g | ||
| Poultry | Calcium | 60–90 g | ||
| Fish | Iron | 60–90 g | ||
| Eggs | Thiamin | 2–3 per week | ||
| Dry beans and peas, cooked |
Riboflavin | 1 – 11/2 cups | ||
| Nuts and seeds | 1/2 – 3/4 cup | |||
| Peanut butter | 4 tbs | |||
| Fats and oil | Use sparingly | Use sparingly | ||
| Butter or margarine |
Fat | 1–2 tbs | ||
| Total kilojoules | 8 400–9 240 | 9 240–10 500 | ||
Harmful substances
Avoid all harmful substances that may put you and your baby at risk, such as drugs, medication, alcohol, smoking and caffeine. You should be careful about taking any of these without consulting your caregiver.
- Avoid diuretics.
- Coffee, tea and bran reduce iron absorption.
- Don’t take vitamin and mineral supplements on your own – ask your doctor as too many can lead to complications.
Click here for more information on hazards to your pregnancy.